In order to choose the optimal treatment, it is important to receive comprehensive and comprehensible information. If radiotherapy has been recommended to you, ask your treating oncologist about all the available irradiation methods as well as treatment-related side effects. These may significantly affect the quality of your life during and after treatment. Our physicians have many years of experience in radiotherapy. Moreover, they are experienced in both standard (photon) and proton radiation therapy and are prepared to answer all of your questions.
Prostate cancer is the most frequent diagnosis treated in proton centres all over the world. The reason for this is the high degree of curability, an effort to reduce late, unwanted side effects and an emphasis on the quality of life.
Proton radiotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer achieves the best dose distributions among available radiotherapeutic techniques; prospective non-randomised studies have proven its high effectiveness and very low toxicity, which has also been confirmed in the group of patients treated at the Proton Therapy Center.
Proton therapy is not a new method; Since 1991, the first exclusively clinical (not academic) workplace located at Loma Linda University, California, USA has treated many tens of thousands of patients diagnosed with prostate cancer using proton therapy. Proton therapy is a technologically mature treatment proven by almost three decades of clinical operation. Over the past two years, there have been many publications describing the results and advantages of protons for a given diagnosis.
Many men refuse testing or treatment for prostate cancer, this is due to the side-effects related to cancer treatments, but delaying testing will result in harder to treat cancer. Make sure you know all there is to know about various treatments and side-effects before you choose a treatment.
After the age of fifty, it should be a matter of course to see a urologist every year.
Those who have a blood relative suffering from prostate cancer should be examined from the age of forty.
Not all men will get symptoms, but if they’re concerned or have a family history make sure you refer them for tests. There is no current screening programme to detect this cancer, however there’s a blood test readily available to test the PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) score which detects signs of prostate cancer.
Contraindications for Proton Radiotherapy
- Metastasis (the cancer has spread from its primary location to other organs) – lymph nodes involvement is typically not a contraindication
- Metal/ceramic parts in the radiation field
- Metal hip replacement implants
- Presence of a pacemaker
Benefits of Proton Therapy
The most important aspect of treating prostate cancer is to destroy the cancer cells without damaging the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Based on the latest published data, following proton therapy, the 5-year survival rate without PSA relapse is 97–99% for low-risk prostate carcinoma, 85–95% for moderate-risk prostate carcinoma, and 75–85% for high-risk prostate carcinoma.
- Proton radiotherapy has minimal toxicity, therefore minimal side effects. Recently published studies describe severe toxicity of treatment in less than 1% of a large population of patients. When compared with published data on conventional (photon) radiotherapy, such toxicity is minimal and significantly lower.
- Unlike surgery, proton therapy has minimal risk of causing impotence, thus significantly enhancing patients’ quality of life.
- In the case of high-risk prostate carcinoma, proton radiotherapy allows for irradiation of the pelvic lymph nodes with high probability of subclinical affection. This clinical situation best reflects the dosimetric and clinical benefits of proton radiotherapy as it causes no harm to organs in the abdominal cavity, in particular the intestinal villi.
- Proton radiotherapy is a fully outpatient treatment. For low- and moderate-risk prostate carcinoma, it is typically possible to use stereotactic radiation lasting 10 days.
PROTON IRRADIATION
PHOTON IRRADIATION
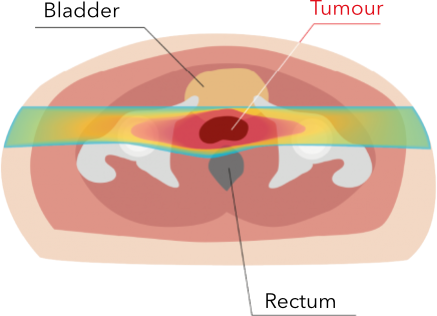
Protons target the tumour directly, sparing healthy tissues and organs from unwanted effects.
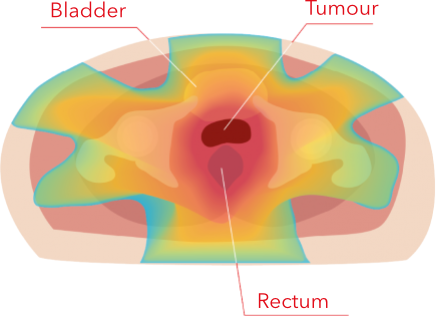
Photons irradiate the tumour as well as the healthy tissues and organs around it.
Reduced risk of incontinence
Radiation to the bladder and surrounding areas can cause incontinence, erectile dysfunction etc. Proton therapy limits the radiation to the tumour itself, increasing the chances of avoiding urinary complications such as involuntary leakage.
Reduced risk of erectile dysfunction
Surgery for prostate cancer can result in erectile dysfunction, which is one of the most common side effects. Due to proton therapy’s targeted approach, studies have found that patients who’ve had proton therapy have a significantly reduced risk of impotence, with 94% of men reporting that they remain sexually active.
Fewer gastrointestinal side effects
Multiple studies have found that proton therapy reduces the risk of gastrointestinal side effects in comparison with IMRT and other radiation techniques. This is because proton therapy significantly decreases the radiation dose to gastrointestinal structures.
Painless, with reduced recovery time
Proton therapy is a relatively painless, non-invasive outpatient procedure. It does not require recovery time and has little or no impact on a patient’s energy levels.
To learn more about proton therapy for prostate cancer, or to find out if you are a suitable candidate for treatment at our centre, contact us today. Our team will get back to you with a detailed response as soon as possible.
