Target volumes, fractionation and the timing of radiotherapy for individual subgroups of pediatric tumours are specified in the respective pediatric protocols. The rule is that the fractionation, volume and dose are the same as in the case of photon radiation therapy. The advantage of proton therapy is the achievement of greater conformity with a lower integral dose.
Primary Paediatric Indications for Proton Therapy
Referral from the paediatric oncologist is required!
- Medulloblastoma: postoperative RT
- Craniopharyngioma: postoperative radiotherapy, radical surgical resection contraindicated in the case of recurrence
- Gliomas with a low degree of malignancy: inoperable oligodendroglioma and astrocytomas, radical radiotherapy in the case of impossibility to perform radical resection, postoperative radiotherapy in R1 or R2 resection
- Ependymoma: postoperative radiotherapy, radiotherapy of recurrent tumours to the extent according to the stage of disease
- Germ cell tumours: to the extent according to the relevant protocol (independently or after chemotherapy)
- High-grade gliomas: recurrent tumours after previous radiotherapy, primarily in unfavourable locations in selected patients
- Chordomas, chondrosarcomas: postoperative/radical radiotherapy
- Soft tissue sarcomas (in unfavourable locations): to the extent according to the relevant protocol
- Ewing’s sarcoma (in unfavourable locations): to the extent according to the relevant protocol
- Any other tumours as specified by a multidisciplinary team (esthesioneuroblastoma, neuroblastoma, nephroblastoma, malignant lymphomas, and others)
The Benefits of Proton Therapy
The treatment protocols employed at PTC are the same internationally accepted protocols that have achieved treatment success world-wide. Proton therapy clearly demonstrates:
- Reduced incidence of secondary malignancies
- Reduced amount of growth abnormalities
- Reduced hormonal dysfunction
- Reduced levels of cognitive impairment
- Reduced incidence of acute adverse effects such as radiation mucositis, pneumonitis, and gastroenteritis
The Advantages of Proton Therapy
Unlike photons, which release maximum energy on the surface and their energy decreases with depth, protons release only a small amount of energy as they pass through the healthy tissues. Just before the end of the proton’s trajectory, the tissue absorbs most of the energy, and there is a sharp increase in the dose (in the tumour) and a subsequent sharp decrease to zero (healthy tissues beyond the tumour). This is called the Bragg peak. The depth at which the Bragg peak occurs is determined by the proton energy.
PROTON IRRADIATION
PHOTON IRRADIATION
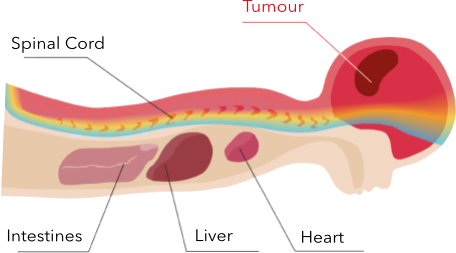
Protons target the tumour directly, sparing healthy tissues and organs from unwanted effects.
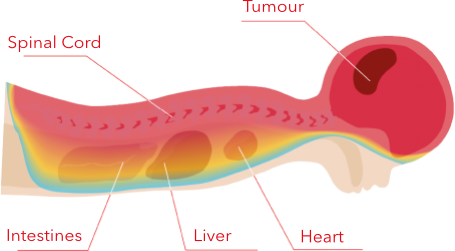
Photons irradiate the tumour as well as the healthy tissues and organs around it.
Proton radiotherapy is associated with the sparing of the tissue “in front of the tumour” (from the perspective of the radiation source) and in particular beyond the tumour. In this way, it is possible to deliver the prescribed dose to the target volume while sparing the healthy tissue (as compared to photon radiation) and improve the quality of life of pediatric patients after treatment.
The percentage of tumours induced by irradiation after proton radiotherapy should drop significantly, since the percentage of irradiated healthy tissue decreases considerably in comparison with photon therapy.
A pediatric patient is admitted for treatment based on a recommendation from their pediatric oncologist. The Proton Therapy Center in Prague cooperates with the Clinic of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology at the University Hospital in Motol, and the Clinic of Pediatric Oncology at the University Hospital in Brno.
To learn more about proton therapy for paediatric cancer, or to find out if you are a suitable candidate for treatment at our centre, contact us today. Our team will get back to you with a detailed response as soon as possible.
* Suitability for treatment at our centre must be determined by our medical team.


